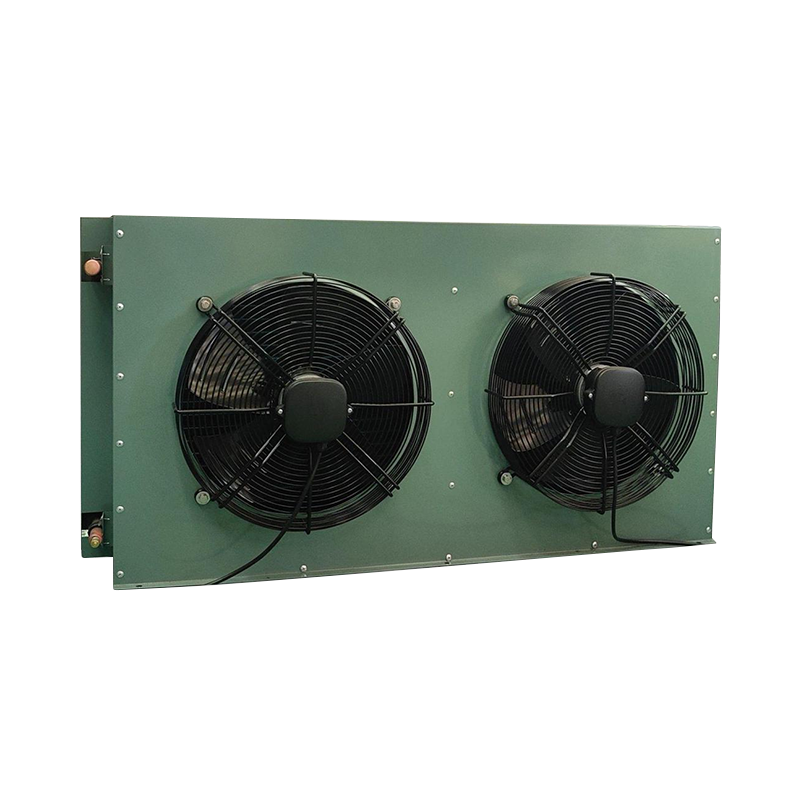
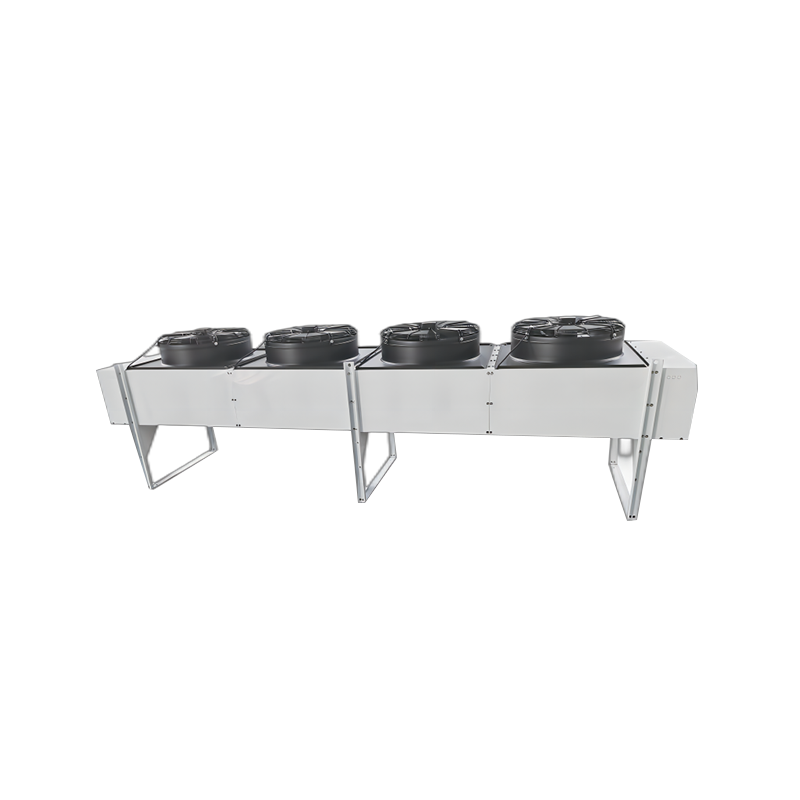
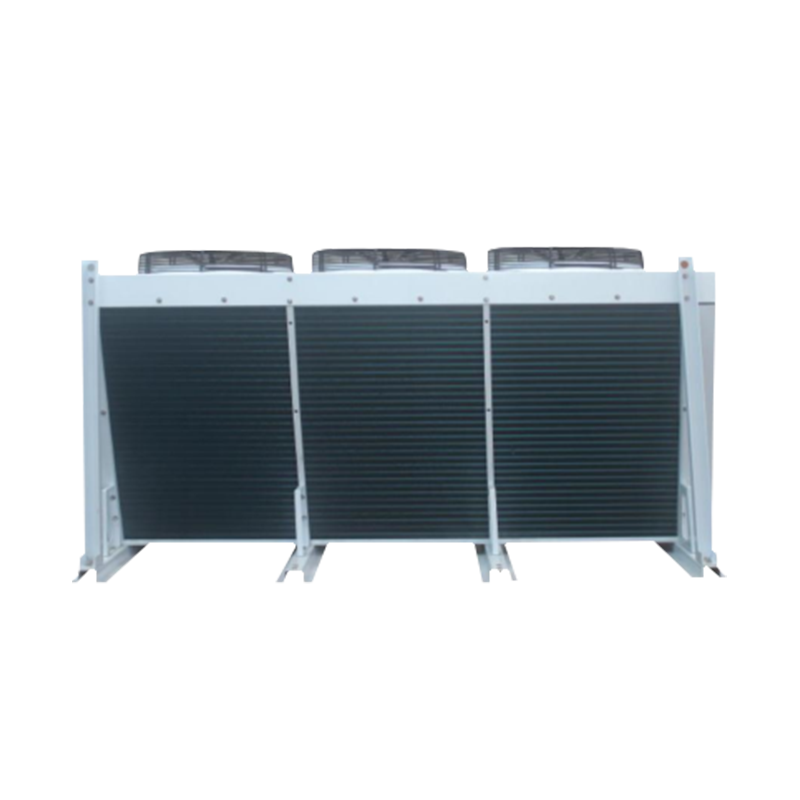
The condenser is a key component in a refrigeration system. Its primary function is to cool high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas and convert it into a liquid state, while simultaneously transferring heat to a cooling medium (such as water, air, or a mixture of water and air) to ensure the proper operation of the refrigeration system.
The condenser operates on the principle of heat exchange. As the refrigerant flows through the condenser's pipes, it exchanges heat with the cooling medium (such as air or water), cooling the refrigerant from gas to liquid and releasing heat to the external environment. The condenser's structure typically includes heat transfer tubes, fins, a housing and support structure, and cooling medium channels.
There are various types of condensers, the most common of which are air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative condensers. Air-cooled condensers use air as the cooling medium, water-cooled condensers use water, and evaporative condensers combine air and water as cooling media to improve cooling efficiency.
The condenser plays a crucial role in the refrigeration system. It not only cools the refrigerant from gas to liquid but also transfers heat to the environment through heat dissipation, ensuring stable operation of the refrigeration system.
What is the difference between a compressor and a condenser?
In a refrigeration system, the compressor and condenser are two core components, with significant differences in their function, structure, and role. Understanding these differences will help you better understand how refrigeration systems work.
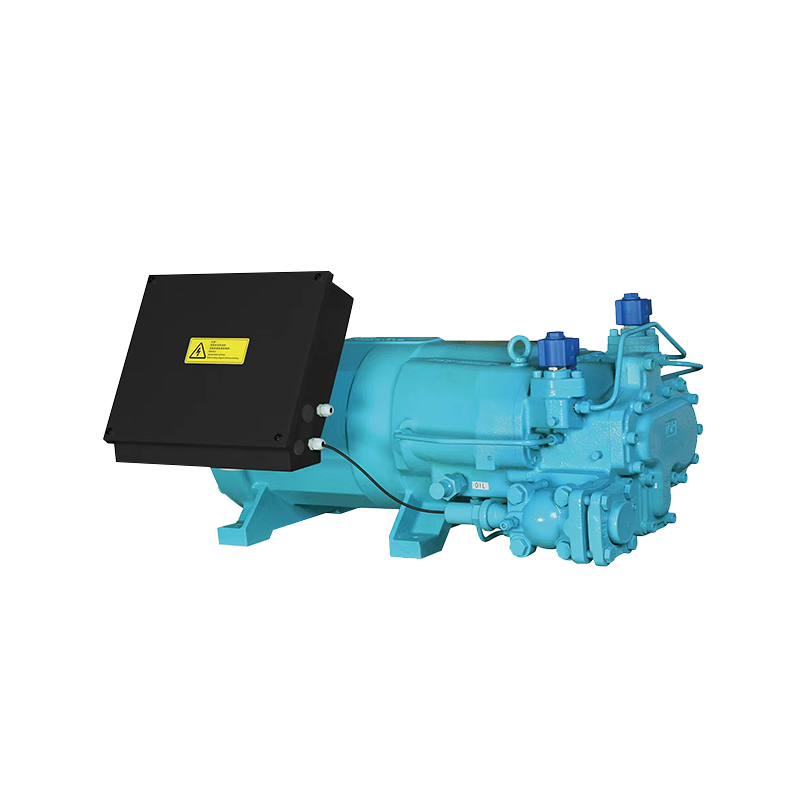
The compressor is the "heart" of the refrigeration system, primarily responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature. The compressor uses mechanical work to compress the low-temperature, low-pressure refrigerant gas into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas, providing power for the refrigerant's circulation. The compressor is typically located in the indoor or outdoor unit of an air conditioning system. Its operation involves components such as a motor and a pump. Compressors come in various types, including reciprocating, rotary, and screw.
The condenser is a heat exchange device that cools the high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas generated by the compressor and converts it into a high-pressure liquid. The condenser releases heat from the refrigerant to the outside environment through heat exchange with the surrounding air or water, thereby achieving cooling. The condenser is typically located outdoors in an air conditioning system. Its structure, including coils, fins, and other components, ensures efficient heat dissipation. Condensers come in various types, including air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative.
Functional Differences: The compressor primarily compresses the refrigerant, raising its pressure and temperature, while the condenser cools the high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas and converts it into liquid, releasing heat. The compressor and condenser each perform different functions in the refrigeration cycle, working together to ensure the proper operation of the refrigeration system.
Location Differences: The compressor is typically located in the indoor or outdoor unit of the air conditioning system, while the condenser is typically located outdoors, adjacent to the compressor.
Operating Principle Differences: The compressor compresses the refrigerant through mechanical work, while the condenser releases heat to the outside environment through heat exchange.
The compressor and condenser each perform different functions in a refrigeration system, working together to complete the refrigeration cycle and ensure proper system operation.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский