Content
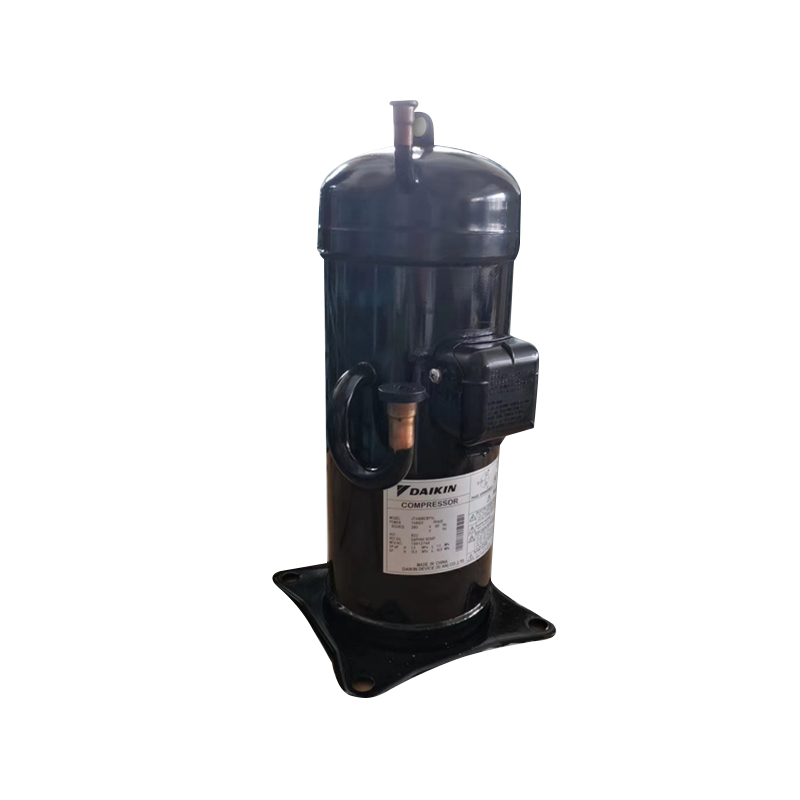
What is a scroll compressor?
A scroll compressor, also known as a scroll-type compressor, is a positive displacement gas compression device. It consists of a fixed scroll and an eccentrically rotating orbiting scroll. These two scrolls mesh together to form a series of crescent-shaped working chambers. This design enables continuous, smooth compression, making it widely used in air conditioning, refrigeration, and air compression.
How does a scroll compressor work?
The operating principle of a scroll compressor can be divided into three stages: suction, compression, and exhaust.
- Suction Stage: As the orbiting scroll rotates, its outer periphery forms an expanded space with the fixed scroll, drawing in low-pressure gas.
- Compression Stage: As the orbiting scroll continues to rotate, the drawn-in gas is trapped within the crescent-shaped compression chamber formed by the two scrolls. As the orbiting scroll rotates toward the center, the chamber volume gradually decreases, increasing the gas pressure and temperature.
- Discharge Phase: After the gas is compressed to a predetermined high pressure, it is discharged through the port located at the center of the fixed scroll.
This cycle is continuous: as one compression chamber discharges, a new suction chamber forms at the periphery, enabling uninterrupted refrigerant or air compression.
Advantages of Scroll Compressors
Scroll compressors offer several advantages due to their operating method:
- High Efficiency: Continuous suction, compression, and discharge reduce gas pulsation and improve efficiency.
- Low Noise and Vibration: With no reciprocating parts, operation is smooth and quieter than piston compressors.
- Compact Structure: Small size and light weight make installation and maintenance easier.
- High Reliability: Fewer moving parts reduce friction and wear, extending service life and lowering maintenance costs.
- Liquid Tolerance: Small amounts of liquid refrigerant can be expelled without damage.
Comparison of Scroll and Screw Compressors
- Operating Principle: Scroll units compress via relative motion of scroll plates; screw units use a pair of intermeshing rotors.
- Applications: Scroll units typically handle smaller displacement—common in home AC, heat pumps, small commercial refrigeration, and air compressors. Screw units suit large commercial AC, chillers, and industrial gas compression with higher flow rates.
- Cost: Scroll units generally have lower manufacturing costs and good cost-effectiveness.
Scroll Compressor Applications
Thanks to their performance and compact design, scroll compressors are used across multiple fields:
- Residential and Commercial Air Conditioning: Many modern split and central systems use scroll compressors for efficient, quiet cooling and heating.
- Heat Pumps: In air-source and water-source systems, they move low-temperature heat to higher-temperature zones.
- Refrigeration: Used in commercial refrigerators, ice machines, and cold storage to maintain freshness.
- Automotive Air Conditioning: Many hybrid and electric vehicles use electric scroll compressors to meet efficiency demands.
- Medical and Industrial: Suitable where clean compressed air is needed, such as lab equipment, medical oxygen generators, and pneumatic tools.
Scroll Compressor Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Monitor operating sound, vibration, and temperature to catch abnormalities early.
- Cleanliness: Keep surroundings clean to avoid dust and debris that can impair heat dissipation.
- System Checks: Ensure proper refrigerant or lubricant quantity and quality; check for leaks at connections.
- Professional Service: For complex faults, seek qualified technicians; avoid disassembly or self-repair.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский