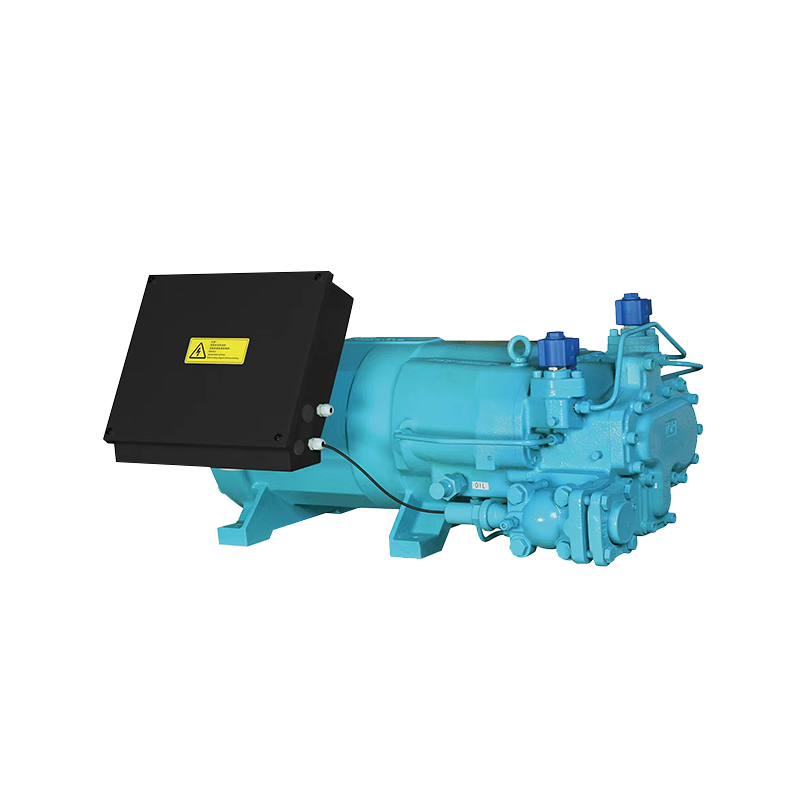
The core differences lie in their structural design, maintainability, power range, and application scenarios. Hermetic compressors adopt a fully sealed, welded structure and are suitable for low-power, maintenance-free applications. Semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors use a detachable casing structure, support repair and maintenance, and are more suitable for medium- to high-power, industrial-grade continuous refrigeration systems. They are widely used in commercial refrigeration and industrial refrigeration fields.
Content
Structural Differences Determine Application Positioning
Hermetic compressor – structural characteristics:
- Fully welded and sealed housing
- Motor and compressor share the same sealed chamber
- Non-serviceable / non-repairable structure
- Integrated one-piece design
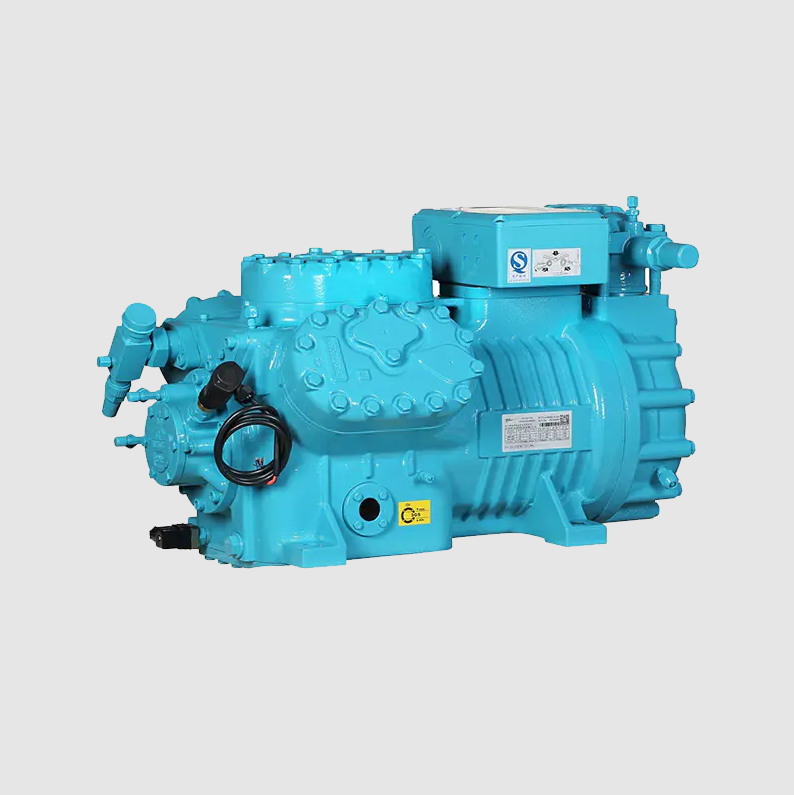

Semi-hermetic refrigeration compressor – structural characteristics:
- Bolted casing structure
- Detachable housing
- Core components can be inspected and replaced
- Modular structural design
Differences in Maintenance and Serviceability
Hermetic compressors: Usually require complete unit replacement after failure, maintenance cost is concentrated in one-time replacement, longer downtime due to full replacement.
Semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors: Support maintenance of bearings, valve plates, motor windings, etc., allow modular/disassembled servicing, controllable and lower long-term maintenance costs.
Engineering example: In a cold storage system, a 30 kW semi-hermetic refrigeration compressor can be restored to service by replacing valve plates, whereas a hermetic compressor usually requires complete scrapping and replacement of the whole unit.
Power Range and Load Capacity Comparison
| Type | Typical Power Range | Load Capacity | Continuous Operation Capability |
| Hermetic compressor | 0.2–5 kW | Low | Moderate |
| Semi-hermetic refrigeration compressor | 5–300 kW | Medium to high | Strong |
Energy efficiency and system adaptability: Semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors are typically equipped with more efficient cooling and lubrication structures: Independently designed oil circuit systems, forced lubrication systems, expandable cooling systems, control systems capable of intelligent upgrades.
Application Scenario Differentiation
Typical applications of hermetic compressors: Household refrigerators, beverage coolers and small display cabinets, residential air conditioners.
Typical applications of semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors: Cold storage engineering systems, food cold-chain systems, pharmaceutical cold storage systems, industrial cooling systems, commercial refrigeration units.
Recommended Selection Scenarios
Choose hermetic compressors for: Low-power systems, household or light commercial equipment, integrated all-in-one devices, projects with low maintenance requirements.
Choose semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors for: Medium to large refrigeration systems, cold storage engineering projects, continuous operation conditions, high-reliability requirements, long-term operational projects.
The essential difference between hermetic compressors and semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors lies in “structural maintainability and system engineering attributes.” Hermetic compressors are more oriented toward consumer-grade equipment applications. Semi-hermetic refrigeration compressors are more oriented toward engineering-grade and industrial-grade system configurations.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский