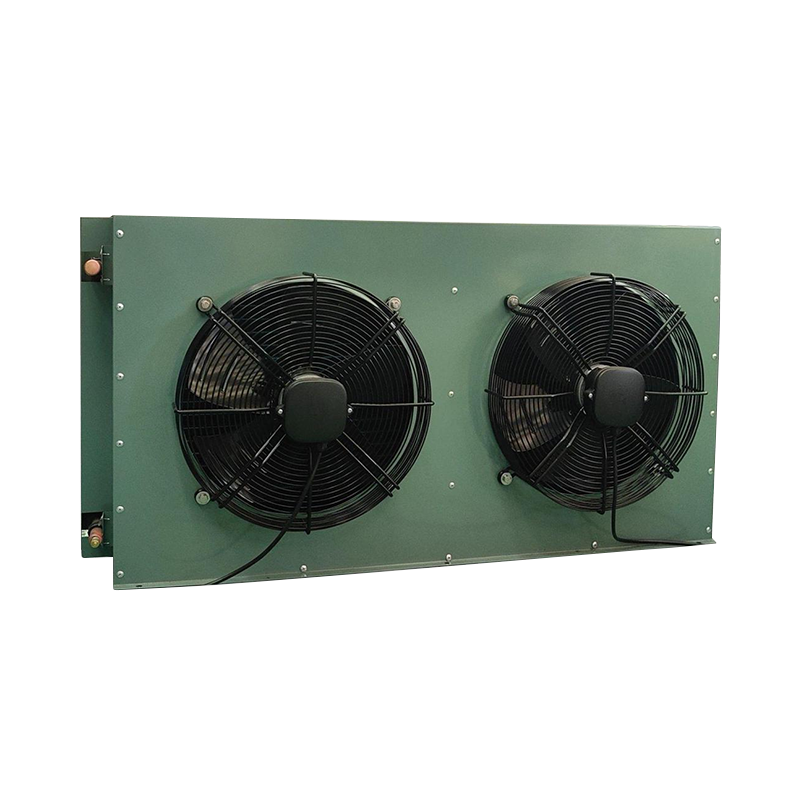
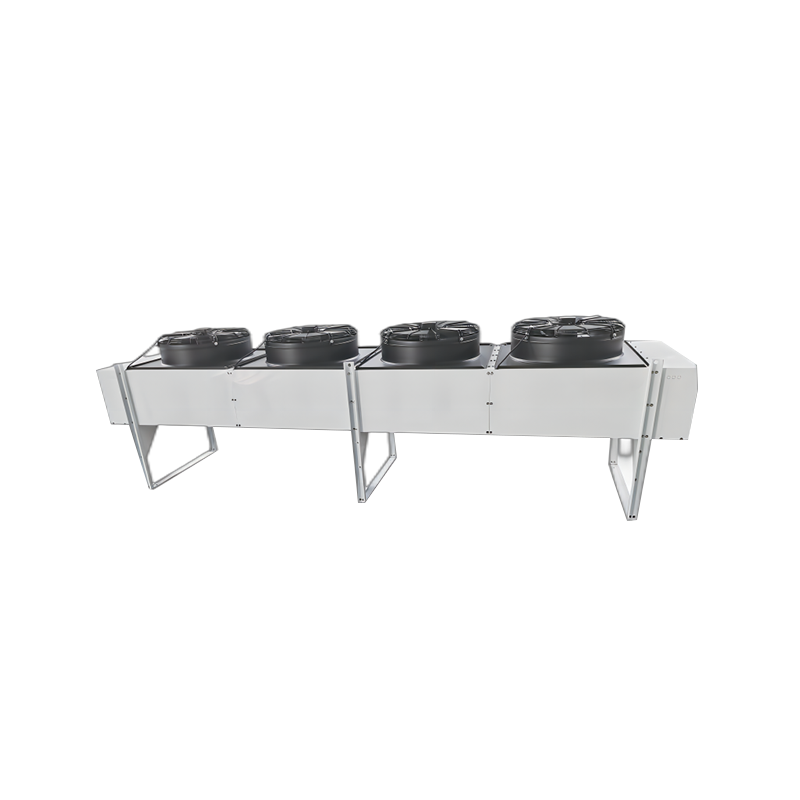
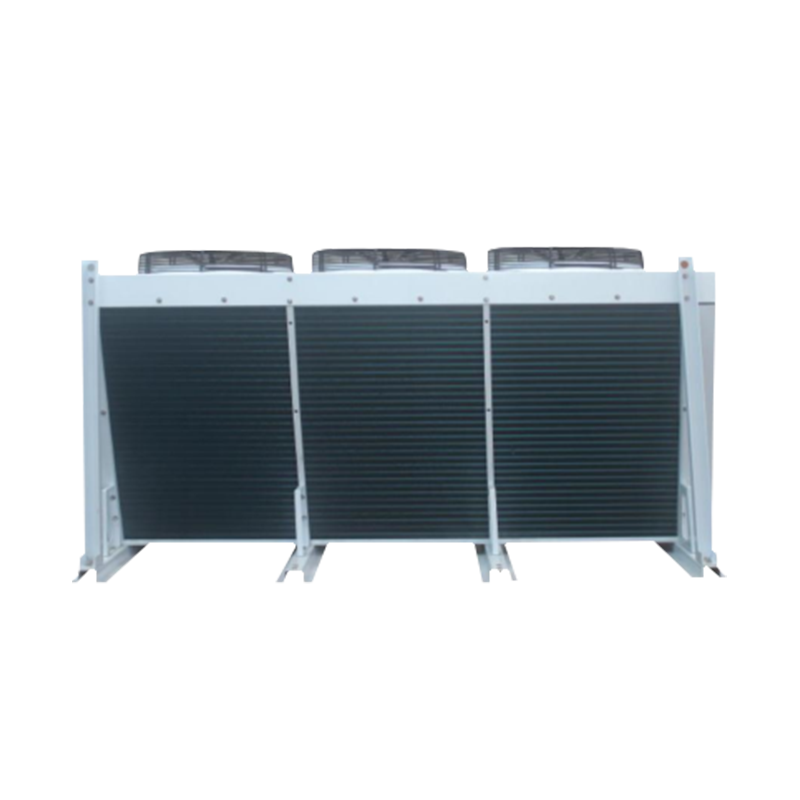
The condenser is a key component in a heat exchange system. Its core function is to convert gas or vapor into liquid while simultaneously dissipating heat. Whether it's a large industrial refrigeration unit or the air conditioners and refrigerators in our homes, condensers play a vital role.
The operation of a condenser is based on the phase change process of matter. In a refrigeration cycle, such as an air conditioning system, the refrigerant is compressed into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas in the compressor. This high-temperature, high-pressure gas is then transported to the condenser.
In the condenser, the hot refrigerant gas exchanges heat with the cooler surrounding medium (usually air or water). This process removes a significant amount of heat from the refrigerant, causing its temperature to drop. When the refrigerant's temperature drops below its saturation temperature, it releases latent heat and condenses into a high-pressure liquid. This gas-to-liquid conversion process is what gives the condenser its name.
Content
Core Functions and Applications of the Condenser
The main functions of a condenser can be summarized as follows:
- Heat Dissipation: This is the most direct function of the condenser. It efficiently dissipates heat absorbed by the system from the room or cooled area to the external environment.
- Refrigerant Phase Change: Converts high-pressure gaseous refrigerant into high-pressure liquid, preparing for the subsequent throttling and expansion process to complete the refrigeration cycle.
- Ensuring Cycle Efficiency: An efficient condenser ensures that heat is quickly and efficiently removed from the system, maintaining the efficiency and stability of the refrigeration or air-conditioning system.
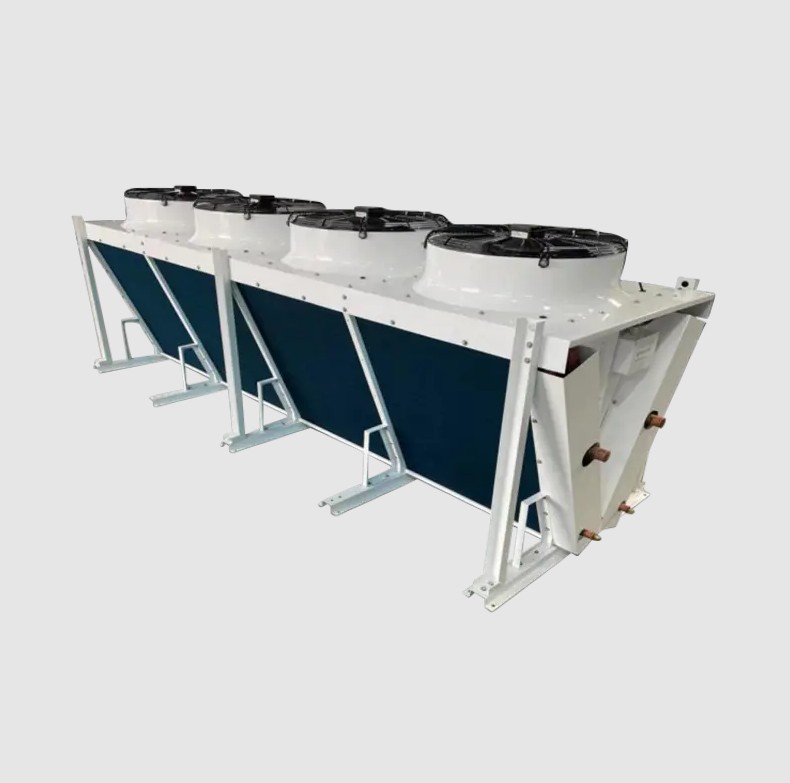

Applications of the Condenser
Condensers are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: In household air conditioners, refrigerators, and commercial cold storage, condensers are the core component for cooling.
- Power Plants: In steam turbine power plants, condensers condense steam after work back into water for reuse.
- Chemical Industry: In processes such as distillation and rectification, condensers are used to recover solvent vapors or separate mixtures.
- Automotive: Automotive air conditioning systems also rely on condensers to cool refrigerant gas.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Condenser in Modern Systems
Whether it's air conditioning for comfortable living or complex machinery that supports industrial processes, condensers are crucial for efficient operation. Understanding the role of condensers not only helps us better understand refrigeration systems but also highlights their crucial role in modern life and industrial development.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский